- September 17, 2015
- Posted by: Surender Kumar
- Category: PowerShell
Manage Services using PowerShell
Table of Contents
As a Windows administrator, you might need to deal with Services on regular basis. You mainly need to list the services, to stop them, and sometimes need to change the Startup Mode. PowerShell offers you various cmdlets which can help you deal with Services. But before start managing the Services, you need to run the PowerShell console with administrator privileges since PowerShell does not violate the Windows security policies; it respects the security policies.
To start, let’s first take a look at the PowerShell cmdlets with the noun “Service” in their name.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Command -Noun Service CommandType Name ModuleName ----------- ---- ---------- Cmdlet Get-Service Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Cmdlet New-Service Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Cmdlet Restart-Service Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Cmdlet Resume-Service Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Cmdlet Set-Service Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Cmdlet Start-Service Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Cmdlet Stop-Service Microsoft.PowerShell.Management Cmdlet Suspend-Service Microsoft.PowerShell.Management
You can use the cmdlets shown above to work with Windows Services.
List all the Services on Your Computer
To list all the services on a computer you can use Get-Service cmdlet (or gsv alias) without any parameter.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running AdobeARMservice Adobe Acrobat Update Service Stopped AeLookupSvc Application Experience Stopped ALG Application Layer Gateway Service Stopped AmmyyAdmin Ammyy Admin Stopped AmmyyAdmin_690 AmmyyAdmin_690 Stopped AppIDSvc Application Identity Running Appinfo Application Information Stopped AppMgmt Application Management Stopped AppReadiness App Readiness Stopped AppXSvc AppX Deployment Service (AppXSVC) Running AudioEndpointBu... Windows Audio Endpoint Builder Running Audiosrv Windows Audio Running AVP15.0.2 Kaspersky Small Office Security Ser... Stopped AxInstSV ActiveX Installer (AxInstSV) Stopped BDESVC BitLocker Drive Encryption Service Running BFE Base Filtering Engine [output cut]
Notice the default behavior of cmdlet is that it lists all the Services in a tabular format having three columns containing Status, Name and DisplayName of each service because Format-Table is the default formatting cmdlet used by Get-Service. This is pretty much satisfactory for most of administrators. But if you want to format the output in List form, you can do this by piping the output of Get-Service cmdlet to Format-List cmdlet (fl alias). The following example lists the services in list format.
PS D:\MyScripts> gsv | fl Name : AdobeARMservice DisplayName : Adobe Acrobat Update Service Status : Running DependentServices : {} ServicesDependedOn : {} CanPauseAndContinue : False CanShutdown : False CanStop : True ServiceType : Win32OwnProcess Name : AeLookupSvc DisplayName : Application Experience Status : Stopped DependentServices : {} ServicesDependedOn : {} CanPauseAndContinue : False CanShutdown : False CanStop : False ServiceType : Win32ShareProcess Name : ALG DisplayName : Application Layer Gateway Service Status : Stopped DependentServices : {} ServicesDependedOn : {} CanPauseAndContinue : False CanShutdown : False CanStop : False ServiceType : Win32OwnProcess Name : AmmyyAdmin DisplayName : Ammyy Admin Status : Stopped DependentServices : {} ServicesDependedOn : {} CanPauseAndContinue : False CanShutdown : False CanStop : False ServiceType : Win32OwnProcess [output cut]
Notice that the output is now displayed in list format. In this format some additional properties are also listed for each service. This is default behavior of Format-List cmdlet. If you want to see specific properties, use -Property parameter followed by the property name in the same order you want to list. The following example with display the all services with 3 properties (Name, DisplayName, Status) in List format.
PS D:\MyScripts> gsv | fl -Property Name, DisplayName, Status Name : AdobeARMservice DisplayName : Adobe Acrobat Update Service Status : Running Name : AeLookupSvc DisplayName : Application Experience Status : Stopped Name : ALG DisplayName : Application Layer Gateway Service Status : Stopped Name : AmmyyAdmin DisplayName : Ammyy Admin Status : Stopped
To display a specific service, use Get-Service cmdlet followed by the name of service. The following example displays the Windows Update service.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service "Windows Update" Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running wuauserv Windows Update
You can also use wildcard (*) to list multiple services starting or ending with same name. The following example lists all the services having microsoft keyword in their name.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service -DisplayName *microsoft* Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Stopped MSiSCSI Microsoft iSCSI Initiator Service Stopped MsKeyboardFilter Microsoft Keyboard Filter Stopped odserv Microsoft Office Diagnostics Service Stopped smphost Microsoft Storage Spaces SMP Stopped swprv Microsoft Software Shadow Copy Prov... Stopped wlidsvc Microsoft Account Sign-in Assistant
Manipulate the Output of Get-Service
Remember that PowerShell provides a Get-Member cmdlet which helps you to list all the properties associated with any cmdlet. Taking advantage of Get-Service | Get-Member, we can refine the output so that we add extra properties, for example, CanStop and ServiceType.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Get-Member TypeName: System.ServiceProcess.ServiceController Name MemberType Definition ---- ---------- ---------- Name AliasProperty Name = ServiceName RequiredServices AliasProperty RequiredServices = ServicesDependedOn Disposed Event System.EventHandler Disposed(System.Object, System.EventArgs) Close Method void Close() Continue Method void Continue() CreateObjRef Method System.Runtime.Remoting.ObjRef CreateObjRef(type requestedType) Dispose Method void Dispose(), void IDisposable.Dispose() Equals Method bool Equals(System.Object obj) ExecuteCommand Method void ExecuteCommand(int command) GetHashCode Method int GetHashCode() GetLifetimeService Method System.Object GetLifetimeService() GetType Method type GetType() InitializeLifetimeService Method System.Object InitializeLifetimeService() Pause Method void Pause() Refresh Method void Refresh() Start Method void Start(), void Start(string[] args) Stop Method void Stop() WaitForStatus Method void WaitForStatus(System.ServiceProcess.ServiceControllerStatus desiredStatus), void Wa... CanPauseAndContinue Property bool CanPauseAndContinue {get;} CanShutdown Property bool CanShutdown {get;} CanStop Property bool CanStop {get;} Container Property System.ComponentModel.IContainer Container {get;} DependentServices Property System.ServiceProcess.ServiceController[] DependentServices {get;} DisplayName Property string DisplayName {get;set;} MachineName Property string MachineName {get;set;} ServiceHandle Property System.Runtime.InteropServices.SafeHandle ServiceHandle {get;} ServiceName Property string ServiceName {get;set;} ServicesDependedOn Property System.ServiceProcess.ServiceController[] ServicesDependedOn {get;} ServiceType Property System.ServiceProcess.ServiceType ServiceType {get;} Site Property System.ComponentModel.ISite Site {get;set;} Status Property System.ServiceProcess.ServiceControllerStatus Status {get;} ToString ScriptMethod System.Object ToString();
The following example illustrates how we can ‘Sort’ the output based on ServiceType rather than the ‘Name’ property.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Sort-Object -Property ServiceType | Format-Table Name, ServiceType, Status, CanStop -AutoSize Name ServiceType Status CanStop ---- ----------- ------ ------- Intel(R) ME Service Win32OwnProcess Running True Intel(R) PROSet Monitoring Service Win32OwnProcess Running True Intel(R) Capability Licensing Service TCP IP Interface Win32OwnProcess Stopped False RpcLocator Win32OwnProcess Stopped False Intel(R) Capability Licensing Service Interface Win32OwnProcess Running True LMS Win32OwnProcess Running True MozillaMaintenance Win32OwnProcess Stopped False TrustedInstaller Win32OwnProcess Stopped False jhi_service Win32OwnProcess Running True vds Win32OwnProcess Stopped False VSS Win32OwnProcess Stopped False FontCache3.0.0.0 Win32OwnProcess Running True wampapache64 Win32OwnProcess Stopped False Fax Win32OwnProcess Stopped False wampmysqld64 Win32OwnProcess Stopped False [output cut]
The -AutoSize parameter produces more sensible column widths.
Filtering the Output
If you are a System administrator, you might want to look at the services which are running and which have stopped. This can be done with the help of Where-Object cmdlet.
The following command will list the services which are stopped.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Stopped"} Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Stopped AeLookupSvc Application Experience Stopped ALG Application Layer Gateway Service Stopped AmmyyAdmin Ammyy Admin Stopped AmmyyAdmin_690 AmmyyAdmin_690 Stopped AppIDSvc Application Identity Stopped AppMgmt Application Management Stopped AppReadiness App Readiness Stopped AppXSvc AppX Deployment Service (AppXSVC) Stopped AxInstSV ActiveX Installer (AxInstSV) Stopped BDESVC BitLocker Drive Encryption Service Stopped BthHFSrv Bluetooth Handsfree Service Stopped bthserv Bluetooth Support Service Stopped COMSysApp COM+ System Application Stopped cphs Intel(R) Content Protection HECI Se... Stopped CscService Offline Files Stopped defragsvc Optimize drives Stopped DeviceInstall Device Install Service Stopped dot3svc Wired AutoConfig Stopped DsmSvc Device Setup Manager [output cut]
Take careful note of the syntax. The Where-Object is enclosed within curly braces. In addition, the $_ notation is used to represent the object being transferred across the pipeline. The .Status is calling the property of current service in pipeline. You can call any property which you have found using Get-Service | Get-Member command. Notice the comparison operator used is equal to (-eq). Windows PowerShell does not use the standard arithmetic comparison operators; instead, it uses operators such as:
- -lt — Less than
- -le — Less than or equal to
- -gt — Greater than
- -ge — Greater than or equal to
- -eq — Equal to
- -ne — Not equal to
- -like — Like; uses wildcards for pattern matching
- -match — Matches a string using regular expressions.
- -contains — Tells whether a collection of reference values includes a single test value. Always returns a Boolean value TRUE or FALSE.
- -replace — Changes the specified elements of a value.
If you want to look for the services which are Running, just replace the ‘Stopped’ keyword with Running in above command. The command is shown below:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"} Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running AdobeARMservice Adobe Acrobat Update Service Running Appinfo Application Information Running AudioEndpointBu... Windows Audio Endpoint Builder Running Audiosrv Windows Audio Running AVP15.0.2 Kaspersky Small Office Security Ser... Running BFE Base Filtering Engine Running BITS Background Intelligent Transfer Ser... Running BrokerInfrastru... Background Tasks Infrastructure Ser... Running Browser Computer Browser [output cut]
You can also filter the output with Select-Object cmdlet using -Property parameter of command as shown below:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Select-Object -Property DisplayName, Status DisplayName Status ----------- ------ Adobe Acrobat Update Service Running Application Experience Running Application Layer Gateway Service Stopped Ammyy Admin Stopped [output cut]
The above commands will only display DisplayName and Status properties of windows services.
Use Get-Service on Remote Computer
You can use Get-Service cmdlet with –ComputerName parameter to retrieve and manipulate the services of remote computer as you did with local computer. You must have enough privileges on remote computer in order to run the command. Also note that Get-Service command does not use PowerShell remoting (WSMan) to retrieve data from remote computer; instead it uses dot net framework methods. So, you can run Get-Service cmdlet against any remote computer which does not have PowerShell remoting configured.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service -ComputerName DC1 Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running ADWS Active Directory Web Services Stopped AeLookupSvc Application Experience Stopped ALG Application Layer Gateway Service Running AppHostSvc Application Host Helper Service Stopped AppIDSvc Application Identity Running Appinfo Application Information Stopped AppMgmt Application Management Stopped aspnet_state ASP.NET State Service Stopped AudioEndpointBu... Windows Audio Endpoint Builder Stopped AudioSrv Windows Audio Running AVP15.0.2 Kaspersky Small Office Security Ser... Running BFE Base Filtering Engine Running BITS Background Intelligent Transfer Ser... [output cut]
Using Out-File cmdlet
You can use Out-File cmdlet to redirect and save the output of Get-Service and even the output of every cmdlet to a text file. This method can be helpful for logging.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Stopped"} | out-file "D:\Stopped_services.txt"
This time you will not see any output on console, instead the output is sent to file D:\Stopped_services.txt file. If you look at the contents of file, the output would be similar to that of console output.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Content D:\Stopped_services.txt Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Stopped AeLookupSvc Application Experience Stopped ALG Application Layer Gateway Service Stopped AmmyyAdmin Ammyy Admin Stopped AmmyyAdmin_690 AmmyyAdmin_690 Stopped AppIDSvc Application Identity Stopped AppMgmt Application Management Stopped AppReadiness App Readiness Stopped AppXSvc AppX Deployment Service (AppXSVC) Stopped AxInstSV ActiveX Installer (AxInstSV) Stopped BDESVC BitLocker Drive Encryption Service Stopped BthHFSrv Bluetooth Handsfree Service Stopped bthserv Bluetooth Support Service Stopped COMSysApp COM+ System Application Stopped cphs Intel(R) Content Protection HECI Se... Stopped CscService Offline Files Stopped defragsvc Optimize drives Stopped DeviceInstall Device Install Service [output cut]
Start a Windows Service
You can start any service with the help of Start-Service cmdlet. An example of starting a ‘Stopped’ windows update service is given below:
PS D:\MyScripts> gsv wuauserv Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Stopped wuauserv Windows Update PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service wuauserv | Start-Service -Verbose VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Start-Service" on target "Windows Update (wuauserv)".
In first command, I checked the status of Windows Update service. I saw it is stopped. So, I piped the output of Get-Service wuauserv command to Start-Service cmdlet and the service started. The -verbose switch displayed the information about the operation being performed.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service wuauserv Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running wuauserv Windows Update
You can also use the Start-Service cmdlet directly if you know the name of service you want to start. This is shown below:
PS D:\MyScripts> Start-Service AmmyyAdmin -Verbose VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Start-Service" on target "Ammyy Admin (AmmyyAdmin)".
Stop a Windows Service
To stop any running service, use Stop-Service cmdlet as shown below:
PS D:\MyScripts> Stop-Service AmmyyAdmin ; Get-Service AmmyyAdmin Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Stopped AmmyyAdmin Ammyy Admin
This time I did not use -verbose switch, that’s why I did not see any information but the service is actually stopped. Notice that I’ve used semi-colon (;) to run two commands at one time. You can always run multiple PowerShell commands at once by using semi-colon (;) between each command.
Change the Service StartMode
Sometime you might want to see and even change the StartMode of any service. The StartMode is a condition which determines the behavior of service. The StartupMode can accept the following values:
- Automatic: The Service is started automatically as part of the Windows boot process.
- Manual: The Service can be started by any application, process or user whenever needed, but is off by default. Once it is started, the service will remain started until it is manually stopped or the system is rebooted.
- Disabled: The service is disabled. It will not run.
Unfortunately, Windows PowerShell does not have any built-in cmdlet which can display the StartMode for any service. The Get-Service cmdlet does not display StartMode property even when used with Format-List -Property * parameter.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service wuauserv | Select-Object -Property * Name : wuauserv RequiredServices : {rpcss} CanPauseAndContinue : False CanShutdown : False CanStop : False DisplayName : Windows Update DependentServices : {} MachineName : . ServiceName : wuauserv ServicesDependedOn : {rpcss} ServiceHandle : SafeServiceHandle Status : Stopped ServiceType : Win32ShareProcess Site : Container :
Look at the output of above command; you can not see the StartMode property. So, how do you come to know if any service (Windows Update for instance) is set to start automatically at system startup or it is set as manual?
Luckily, Windows PowerShell has a Get-WmiObject cmdlet which allows you to query WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) on system and retrieve the data from WMI store. You can see the StartMode property of any windows service using Get-WmiObject cmdlet as shown below:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Service ExitCode : 0 Name : AdobeARMservice ProcessId : 1532 StartMode : Auto State : Running Status : OK ExitCode : 0 Name : AeLookupSvc ProcessId : 0 StartMode : Manual State : Stopped Status : OK ExitCode : 1077 Name : ALG ProcessId : 0 StartMode : Manual State : Stopped Status : OK [output cut]
Notice that Get-WmiObject cmdlet by default uses Format-List to format the output and it displays all the information like that of Get-Service cmdlet including StartMode property. To display the output in the same format as Get-Service; use the following command:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Service | Format-Table -Property State, Name, DisplayName, StartMode State Name DisplayName StartMode ----- ---- ----------- --------- Running AdobeARMservice Adobe Acrobat Update Service Auto Stopped AeLookupSvc Application Experience Manual Stopped ALG Application Layer Gateway Ser... Manual Stopped AmmyyAdmin_690 [output cut]
The above command produces the output similar to Get-Service cmdlet including StartMode property for every service.
To view the StartMode property for a particular service (Windows Update for instance), use the Get-WmiObject cmdlet as shown below:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Service | Where-Object {$_.name -eq 'wuauserv'} | Format-Table -Property State, Name, Di splayName, StartMode State Name DisplayName StartMode ----- ---- ----------- --------- Running wuauserv Windows Update Manual
You see the above command became very lengthy. You can always shorten the commands by using aliases instead of typing complete command. The above command can be shortened as follows:
PS D:\MyScripts> gwmi Win32_Service|?{$_.name -eq 'wuauserv'}|ft State,Name,DisplayName,StartMode
State Name DisplayName StartMode
----- ---- ----------- ---------
Stopped wuauserv Windows Update Manual
Now, we know that Windows update service has StartMode set to Manual. To change the StartMode, use Set-Service cmdlet with -StartupType parameter as shown below:
PS D:\MyScripts> Set-Service wuauserv -StartupType Automatic -Status Running PS D:\MyScripts> gwmi Win32_Service|?{$_.name -eq 'wuauserv'}|ft State,Name,DisplayName,StartMode State Name DisplayName StartMode ----- ---- ----------- --------- Running wuauserv Windows Update Auto
The -StartupType parameter can accept only 3 values (Automatic, Manual, Disabled) and the -Status parameter can also accept only 3 values (Running, Paused, Stopped).
Stop a Windows Service
You can stop a running windows service using Stop-Service cmdlet. Remember that there are some critical windows services which do not support stopping. To get the list of windows services which can be stopped, use the Get-Service cmdlet as shown below:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq 'Running' -and $_.CanStop} Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running AdobeARMservice Adobe Acrobat Update Service Running Appinfo Application Information Running AudioEndpointBu... Windows Audio Endpoint Builder Running Audiosrv Windows Audio Running AVP15.0.2 Kaspersky Small Office Security Ser... Running BFE Base Filtering Engine Running BITS Background Intelligent Transfer Ser... Running Browser Computer Browser Running c2cautoupdatesvc Skype Click to Call Updater Running c2cpnrsvc Skype Click to Call PNR Service Running CertPropSvc Certificate Propagation Running CryptSvc Cryptographic Services [output cut]
To list all services that cannot be stopped, slightly modify the above command:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.status -eq 'running' -and !$_.CanStop}
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running BrokerInfrastru... Background Tasks Infrastructure Ser...
Running DcomLaunch DCOM Server Process Launcher
Running LSM Local Session Manager
Running Power Power
Running RpcEptMapper RPC Endpoint Mapper
Running RpcSs Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
Running SamSs Security Accounts Manager
Running wudfsvc Windows Driver Foundation - User-mo...
Notice that I used Not Operator (!) in front of CanStop property. The same command could be written as follows:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq 'Running' -and $_.CanStop -eq $false}
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running BrokerInfrastru... Background Tasks Infrastructure Ser...
Running DcomLaunch DCOM Server Process Launcher
Running LSM Local Session Manager
Running Power Power
Running RpcEptMapper RPC Endpoint Mapper
Running RpcSs Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
Running SamSs Security Accounts Manager
Running wudfsvc Windows Driver Foundation - User-mo...
For example, to stop Windows Update service, run the following command:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service wuauserv | Stop-Service -Verbose VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Stop-Service" on target "Windows Update (wuauserv)". WARNING: Waiting for service 'Windows Update (wuauserv)' to stop... WARNING: Waiting for service 'Windows Update (wuauserv)' to stop...
The -verbose switch is used to display the information about the operation being performed. You could also use Stop-Service wuauserv command. Both will work and perform same thing.
Restart a Windows Service
PowerShell gives you Restart-Service cmdlet which works pretty much same way as that of Stop-Service and Start-Service cmdlets. The following example shows how to restart Windows Update service.
PS D:\MyScripts> Restart-Service wuauserv -Verbose VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Restart-Service" on target "Windows Update (wuauserv)".
Pause and Resume Windows Service
The Suspend-Service cmdlet sends a suspend (pause) message to the Windows Service Controller for each of the specified services. While suspended, the service is still running, but its action is halted until resumed, such as by using Resume-Service. You can specify the services by their service names or display names, or you can use the InputObject parameter to pass a service object representing the services that you want to suspend.
The following command list all of the services on the computer that can be suspended.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.CanPauseAndContinue } Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running LanmanWorkstation Workstation Running Netlogon Netlogon Running stisvc Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) Running Winmgmt Windows Management Instrumentation
To Suspend (pause) the Workstation service on computer, use the following command.
PS D:\MyScripts> Suspend-Service -DisplayName Workstation
Now the status service changed to Paused.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service Workstation Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Paused LanmanWorkstation Workstation
To Resume the service, use Resume-Service cmdlet as shown below:
PS D:\MyScripts> Resume-Service -DisplayName Workstation
Using Out-GridView cmdlet
PowerShell offers an Out-GridView cmdlet that sends the output to an interactive graphical table in a separate window. You can use Out-GridView along with Get-Service cmdlet to control services even more elegantly. See the following command as an example:
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.status -eq 'Stopped'} | Out-GridView -Title "Select service(s) to start" –PassThru | Start-Service –Verbose
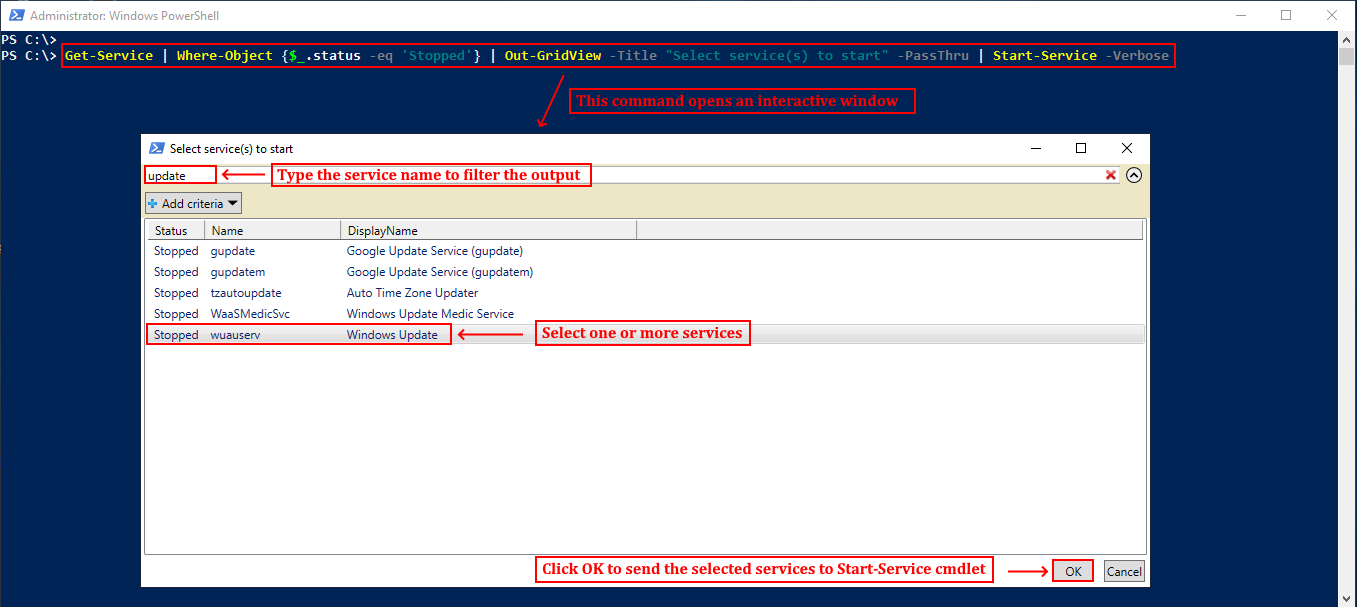
We are essentially getting the services that are currently stopped, passing them to Out-GridView cmdlet in a nice graphical table, where we can select one or more services (by pressing and holding Ctrl button). After making the selection, when we click OK, the selected services will then be passed to Start-Process cmdlet with the help of -PassThru parameter. Ultimately, the selected services will be started. You can use the same idea to stop running services.
Create a new Windows Service
The New-Service cmdlet creates a new entry for a Windows service in the registry and in the service database. A new service requires an executable file that executes during the service.
The parameters of this cmdlet let you set the display name, description, startup type, and dependencies of the service.
For example, I have downloaded a portable TFTP Server from internet and I want to create a new TFTP service on my computer. Use the following PowerShell command to create new service.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service | ? {$_.DisplayName -like "*tftp*"}
This command confirms if there is any existing service on computer with matching name.
The following command creates a new service with the name TFTPServer and sets the StartMode to Manual:
PS D:\MyScripts> New-Service -Name TFTPServer -BinaryPathName "C:\TFTP\tftpd32.exe" -DisplayName "TFTP Server" -Description "Open Source TFTP Server" -StartupType Manual Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Stopped TFTPServer TFTP Server
The newly created service is stopped. To start the service, use Start-Service cmdlet.
PS D:\MyScripts> Start-Service TFTPServer -Verbose
Delete or Remove a Windows Service
Have you ever encountered in a situation when you have uninstalled any software but the it’s rellevant service keeps appearing in Windows Services? The service no longer work and you want to remove this service.However, Windows PowerShell does not give any Remove-Service cmdlet to use, but still you can use Get-WmiObject cmdlet to remove the service. Wodering how?
This is how you do it. Remember that you can create any variable in PowerShell using dollar ($) symbol. You need to create a $svc variable and store the service name into it. Then you need to call delete method and the service will be gone.
I will show you step by step process:
1). Create a $svc variable and store the service with the name TFTServer into it.
PS D:\MyScripts> $svc = Get-WmiObject Win32_Service -Filter "Name='TFTPServer'"
2). To confirm, type the variable name ($svc) and press Enter.
PS D:\MyScripts> $svc ExitCode : 0 Name : TFTPServer ProcessId : 0 StartMode : Manual State : Stopped Status : OK
3). Now you know that the service you want to remove is stored into $svc variable, use Get-Member cmdlet with -MemberType Method parameter to see the available methods for this service. The following command tells you what methods this service can accept.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Member -InputObject $svc -MemberType Method TypeName: System.Management.ManagementObject#root\cimv2\Win32_Service Name MemberType Definition ---- ---------- ---------- Change Method System.Management.ManagementBaseObject Change(System.String DisplayName, System.String PathName... ChangeStartMode Method System.Management.ManagementBaseObject ChangeStartMode(System.String StartMode) Delete Method System.Management.ManagementBaseObject Delete() GetSecurityDescriptor Method System.Management.ManagementBaseObject GetSecurityDescriptor() InterrogateService Method System.Management.ManagementBaseObject InterrogateService() PauseService Method System.Management.ManagementBaseObject PauseService() ResumeService Method System.Management.ManagementBaseObject ResumeService() [output cut]
4). We are only interested in delete method since we want to delete the service. Now, all you need to do is to call the delete method and the service will be removed. This is done with the following command.
PS D:\MyScripts> $svc.delete()
__GENUS : 2
__CLASS : __PARAMETERS
__SUPERCLASS :
__DYNASTY : __PARAMETERS
__RELPATH :
__PROPERTY_COUNT : 1
__DERIVATION : {}
__SERVER :
__NAMESPACE :
__PATH :
ReturnValue : 0
PSComputerName :
5). Use the Get-Service cmdlet to confirm if the service is deleted or still exists.
PS D:\MyScripts> Get-Service TFTPServer Get-Service : Cannot find any service with service name 'TFTPServer'. At line:1 char:1 + Get-Service TFTPServer + ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ + CategoryInfo : ObjectNotFound: (TFTPServer:String) [Get-Service], ServiceCommandException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : NoServiceFoundForGivenName,Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.GetServiceCommand
The above process is not so difficult. But if you believe in shorthand one-liners, below is a one-liner to delete a service:
PS D:\MyScripts> (Get-WmiObject Win32_Service -Filter "Name='TFTPServer'").Delete()
__GENUS : 2
__CLASS : __PARAMETERS
__SUPERCLASS :
__DYNASTY : __PARAMETERS
__RELPATH :
__PROPERTY_COUNT : 1
__DERIVATION : {}
__SERVER :
__NAMESPACE :
__PATH :
ReturnValue : 0
PSComputerName :
The more you use Windows PowerShell, the more you will be able to understand it. Try to use aliases to shorten the commands and use tab-completion feature where-ever possible.
Thats all about Managing windows services using PowerShell. In the next section, we will look into how to Manage Windows Processes using PowerShell.


